Best Fertilizers To Use For Cassava – Why They Are Important And How To Improve Cassava Production For Farmers
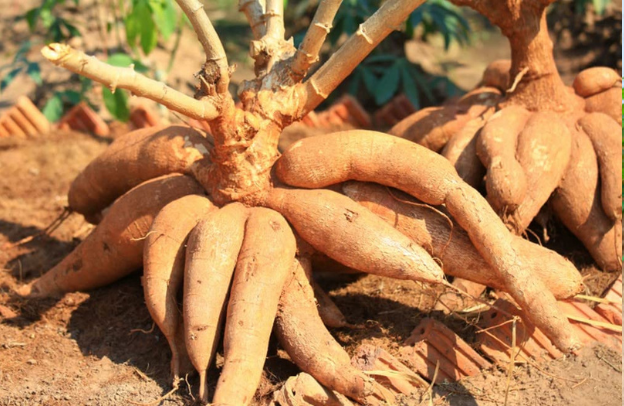

Cassava is a vital staple crop for millions of farmers worldwide, but achieving optimal yields requires more than just planting. The right fertilizers play a crucial role in boosting cassava production by ensuring the soil has the necessary nutrients for healthy growth.
Learn How to Leverage Your Story through our Story To Asset Framework.
In this guide, we’ll explore the best fertilizers for cassava, highlighting their importance in enhancing productivity and providing practical tips on how farmers can improve their cassava farming practices for better results. According to different studies, cassava is the sixth most important food crop globally, and Africa is the world’s largest producer.
In Africa, cassava is the second most important food crop after maize. Its climate-resilient nature makes it an attractive crop for farmers in frost-free areas, including South Africa, where it’s gaining popularity among farming communities.
Cassava’s ability to feed millions hinges on understanding the critical role of fertilizers in its production. By recognizing the importance of fertilizers, farmers can unlock cassava’s full potential, ensuring optimal yields, food security, and sustainable agriculture practices.
See also: Cassava Starch: A Golden Opportunity for African Entrepreneurs in the Global Agribusiness Landscape
The Importance of Fertilizers in Cassava Cultivation
Fertilizers are the lifeblood of modern agriculture, replenishing essential nutrients that crops extract from the soil. For cassava, which thrives in diverse soil conditions, the judicious use of fertilizers can markedly enhance root development and overall yield.
Key Nutrients for Cassava Growth
Cassava plants require a balanced supply of macronutrients:
- Nitrogen (N): Promotes vigorous leaf and stem growth, crucial during the early stages.
- Phosphorus (P): Essential for root development and energy transfer within the plant.
- Potassium (K): Enhances disease resistance and improves the quality of tubers.
A deficiency in any of these can lead to stunted growth and reduced yields.
Selecting the Best Fertilizers for Cassava
Choosing the appropriate fertilizer involves understanding soil composition and the specific needs of the cassava crop. Both inorganic and organic fertilizers have roles to play:
Inorganic Fertilizers:
These are synthesized to provide specific nutrient ratios. Common formulations for cassava include NPK blends such as 15-15-15 or 20-10-10, supplying balanced nutrients essential for growth. Application rates and timing should be guided by soil tests to prevent over-fertilization.
Organic Fertilizers:
Derived from natural sources like compost, manure, or bone meal, these improve soil structure and microbial activity. While they release nutrients more slowly than inorganic options, they enhance long-term soil fertility and sustainability.
See also: Preventing Soil-Borne Diseases in Cassava Farming: Crop Rotation Strategies for Nigerian Farmers
Optimizing Fertilizer Application
To maximize the benefits of fertilization:
Soil Testing:
According to N Extension, before planting, conduct soil tests to determine existing nutrient levels and pH. This information guides the selection and quantity of fertilizers needed.
- Application Timing: Initial fertilization should occur at planting or shortly after, providing young plants with necessary nutrients. Subsequent applications can be timed to coincide with key growth stages, such as tuber development.
- Application Methods: Fertilizers can be applied in bands beside the planting rows or broadcasted evenly across the field. Incorporating fertilizers into the soil minimizes nutrient loss and enhances availability to plant roots.
Improving Cassava Production: Beyond Fertilization
While fertilizers play a vital role in cassava production, several other practices can significantly impact yields, quality, and overall sustainability. By adopting a holistic approach to cassava cultivation, farmers can unlock the full potential of this versatile crop.
Quality Planting Material: The Foundation of a Successful Crop
Using disease-free, high-yielding cassava varieties is essential for achieving optimal results. Selecting healthy stem cuttings from vigorous plants ensures robust growth and sets the stage for a successful crop.
- Disease-free planting material: Ensure that the planting material is free from diseases such as cassava mosaic virus, cassava brown streak virus, and bacterial blight.
- High-yielding varieties: Choose varieties that have been bred for high yields, disease resistance, and adaptability to local conditions.
- Healthy stem cuttings: Select stem cuttings from vigorous plants with a good balance of leaves and stems.
Weed Management: Reducing Competition for Resources
Weeds compete with cassava for essential resources like nutrients, water, and light. Regular weeding, especially during the first few months after planting, is crucial to reduce competition and promote healthy crop development.
- Regular weeding: Weeding should be done regularly, ideally every 1-2 weeks, to prevent weeds from competing with cassava.
- Mulching: Mulching can help suppress weed growth and retain soil moisture.
- Cultural controls: Use cultural controls like crop rotation, sanitation, and pruning to prevent weed growth.
Pest and Disease Control: Protecting Your Crop
Monitoring for common pests and diseases allows for timely interventions. Integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, including the use of resistant varieties and biological controls, can mitigate losses.
- Monitoring: Regularly monitor your crop for signs of pests and diseases.
- Resistant varieties: Use cassava varieties that have been bred for resistance to specific pests and diseases.
- Biological controls: Use biological controls like parasites, predators, and pathogens to manage pest populations.
- Cultural controls: Use cultural controls like sanitation, pruning, and crop rotation to prevent pest and disease spread.
Water Management: Optimizing Moisture Levels
Although cassava is drought-tolerant, consistent moisture supports optimal growth. Implementing irrigation during dry periods can enhance yields.
- Soil moisture monitoring: Monitor soil moisture levels regularly to determine when irrigation is necessary.
- Irrigation: Implement irrigation systems that deliver water directly to the roots, reducing evaporation and runoff.
- Mulching: Mulch around plants to retain soil moisture and reduce evaporation.
By implementing these practices, cassava farmers can improve yields, reduce losses, and promote sustainable production.
See also: Nigerian Cassava Production: How to Transform a Staple Crop into Africa’s Economic Powerhouse
Economic and Environmental Considerations in Cassava Fertilization
Balancing the economic costs of fertilizers with the expected increase in yield is crucial for sustainable cassava production. The delicate balance between fertilizer application and yield optimization must be carefully managed to avoid diminishing profits and environmental degradation.
The Economic Imperative
Cassava farmers must weigh the costs of fertilizers against the potential benefits of increased yields. Over-application of fertilizers can lead to:
- Diminished profits: Excessive fertilizer use can erode profit margins, making cassava production economically unsustainable.
- Inefficient resource allocation: Over-reliance on fertilizers can divert resources away from other essential farming practices, such as irrigation, pest management, and soil conservation.
Under-application of fertilizers can lead to suboptimal yields, which can negatively impact the economic viability of cassava production. Without sufficient fertilizer, crop growth may be stunted, resulting in lower yields. This, in turn, can reduce farmers’ competitiveness in the market, as those who do not optimize fertilizer use may face challenges in keeping up with more efficient producers, ultimately affecting their incomes and livelihoods.
The Environmental Implications
The environmental implications of cassava fertilization must also be carefully considered. Over-application of fertilizers can lead to:
- Nutrient runoff: Excess nutrients from fertilizers can leach into waterways, contributing to eutrophication, algal blooms, and aquatic ecosystem degradation.
- Soil degradation: Over-reliance on fertilizers can lead to soil acidification, nutrient imbalances, and reduced fertility, compromising the long-term sustainability of cassava production.
To mitigate these environmental risks, it is essential to adopt precision fertilizer application practices, guided by:
- Soil testing: Regular soil testing to determine nutrient levels, pH, and other soil parameters.
- Tailored recommendations: Fertilizer application recommendations tailored to specific soil types, crop varieties, and local climate conditions.
Balancing economic and environmental considerations, cassava farmers can optimize fertilizer use, reduce waste, and promote sustainable production practices that ensure the long-term viability of this vital crop.
See also: Cassava: A Sustainable Solution to Combat Food Insecurity in Nigeria
Conclusion
Enhancing cassava production is a multifaceted endeavor, with fertilizers playing a central role in unlocking the crop’s potential.
By selecting appropriate fertilizers, applying them judiciously, and integrating sound agronomic practices, farmers can achieve substantial improvements in yield and quality. Investing in soil health and balanced nutrition not only boosts productivity but also contributes to the long-term sustainability of cassava farming systems.
Learn How to Leverage Your Story through our Story To Asset Framework.